Wheel Chair Lift Design
Using linkages, design a wheel chair lift under a set of physical constraints
The “Chairway to Heaven” project aims to solve a significant accessibility challenge: designing a wheelchair lift that allows seamless vertical movement in residential garages with a height difference of one meter. This project explores the innovative approach used to create a compact, efficient, and user-friendly lift solution.
The Design Vision
The project team sought to create a lift mechanism that is both space-efficient and compliant with Federal ADA regulations. By focusing on simplicity and functionality, we developed a multi-scissor linkage lift that optimizes vertical displacement while maintaining a minimal footprint. Key specifications include supporting a 300-pound load and ensuring smooth operation within 10 seconds for a one-meter elevation.
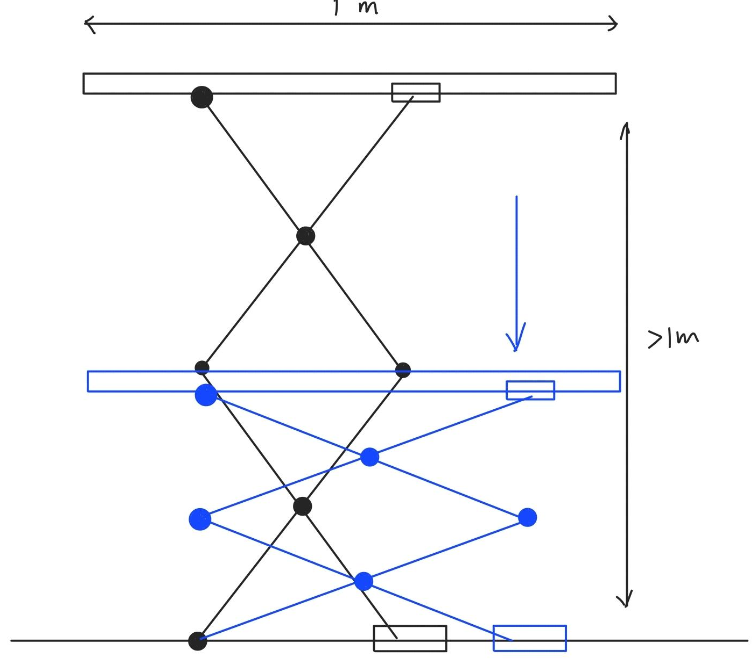
Why a Multi-Scissor Linkage?
The multi-scissor linkage design was chosen for its compactness and scalability. By stacking scissor mechanisms, the design doubles vertical displacement without increasing the overall size. This innovative setup ensures:
- Smooth Translation: The design ensures a horizontal platform throughout its motion.
- Compact Footprint: Ideal for tight residential spaces.
- Efficiency: Less force is required for equivalent elevation compared to traditional designs.
Prototyping
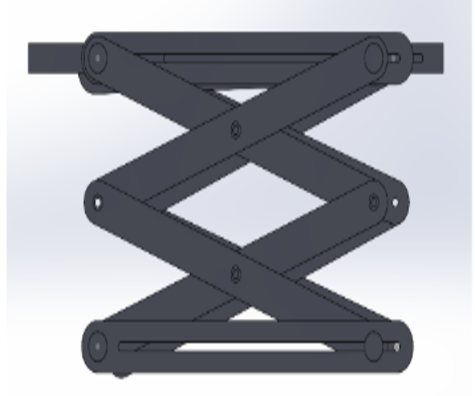
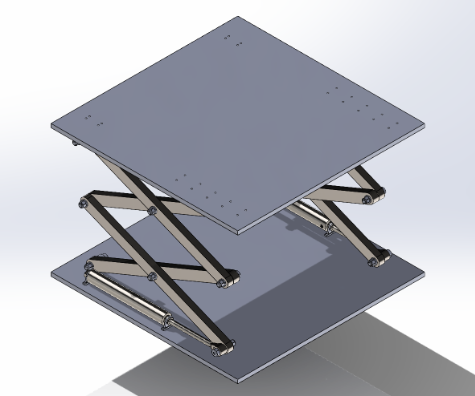
Kinematic Analysis
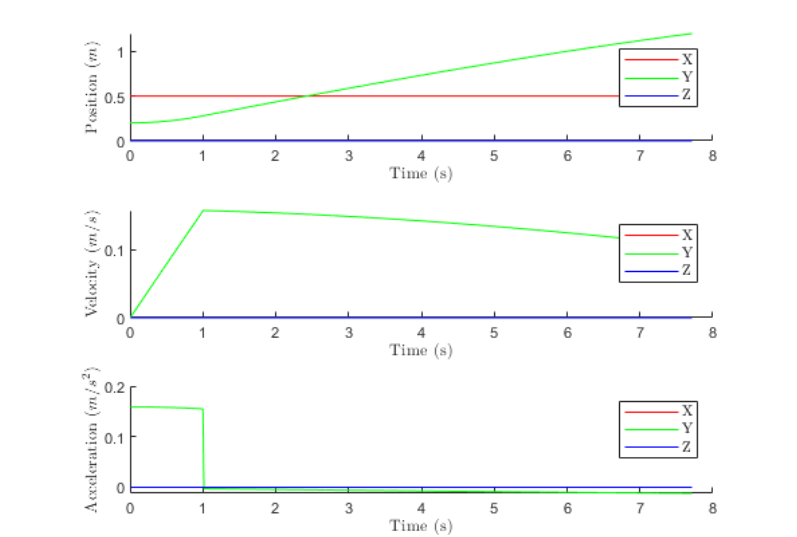
The kinematic analysis focused on ensuring smooth and controlled motion for the lift platform. By using vector equations, the position, velocity, and acceleration of the platform’s center of mass were derived as functions of time. This approach confirmed that the lift meets velocity and acceleration limits of 0.158 m/s and 0.159 m/s², respectively, ensuring user safety and comfort. A MATLAB simulation demonstrated the platform’s predictable movement trajectory, which minimizes any abrupt changes during operation.
Key insights include:
- The lift’s movement follows a stable vertical trajectory, with minimal horizontal deviation.
- The mechanism maintains a horizontal platform orientation throughout the motion cycle, complying with ADA requirements.
Kinetics and Failure Analysis
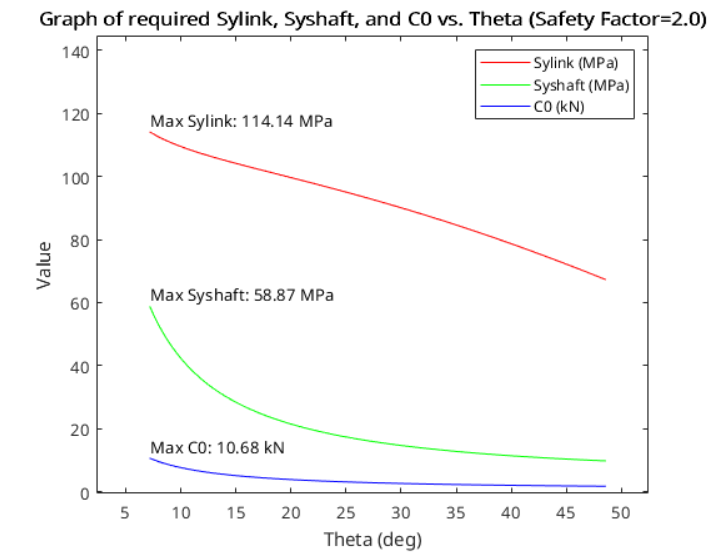
The kinetics analysis evaluated the forces, moments, and stresses acting on the lift components to ensure structural integrity. Using free-body diagrams and equilibrium equations, the team identified high-stress areas, particularly at the central pin and bearing locations. The analysis revealed the following:
- Stress Distribution: The maximum stresses occur at the center of the linkage due to bending moments. This necessitated using 202 annealed stainless steel for its high yield strength (260 MPa).
- Load Capacity: Bearings and shafts were selected to exceed the maximum static and dynamic loads, ensuring durability.
- Safety Factor: A safety factor of 2 was applied to all critical components to accommodate unexpected loads and material inconsistencies.
Conclusion
The “Chairway to Heaven” lift is a testament to engineering innovation and user-centric design. By leveraging advanced analysis tools and iterative refinement, the project delivers a solution that enhances accessibility and independence for individuals with mobility challenges. This lift not only bridges physical gaps but also paves the way for more inclusive residential spaces.